Fibre is a new desktop fiber composite 3D printer launched by 3D printer manufacturer Desktop Metal It uses industrial-grade composite structure 3D printing technology to create high-precision, high-strength and high-stiffness composite parts through continuous fibers
Summary
Summary
Advantage
Advantage
If the video does not play, please allow the browser to run Flash
Fiber Printer Specification
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fiber Printer Applications
 |
 |
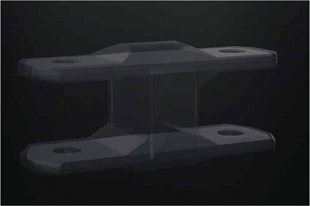
Industrial Manufacturing Fixtures and Fixtures
|
Applications in extremely high temperature environments
|
 |
 |
|
Alternative to aluminum or steel parts 2 times stronger than steel partsOnly 1/2 the weight of aluminum parts |
Antistatic Nylon 6 + carbon fiber and PEKK polyetherketone ketone + carbon base materialFibers meet antistatic standards Tensile strength > 30 times that of ABS material |
How Fiber Printers Work
 |
 |
 |
| Melt Extrusion Process ——FFF coiled wire printing method |
Microfacet automatic tiling process (µAFP) ——Reinforced continuous fiber belt pressure roller printing |
Mechanical Analysis of Printed Pieces ——Analysis of special software for printing |
Fiber Printer Consumables Library
|
Fiber coiled wire (FFF)
|
PEKK polyetherketoneketone Low cost material Excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance and surface wear |
|
Continuous fiber tape (µAFP microfacet fiber tiling technology)
|
Carbon Fiber (CF) High strength and stiffness Low cost |